9654. Depth first search on a disconnected graph
Undirected disconnected
graph is given. Run depth first search on it. For each vertex print the
timestamps when it becomes gray / black in the order of their first
visit.
Input.
First line contains number of vertices n
(n ≤ 100) of undirected
graph. Each next line contains two vertices a and b – an undirected edge of the
graph.
Output. Run depth first search on a graph. For each
vertex print the timestamps when it becomes gray / black in
the order of their first visit.
|
Sample input |
Sample output |
|
6 1 2 5 6 2 4 1 4 |
Vertex: 1, Gray: 1, Black 6 Vertex: 2, Gray: 2, Black 5 Vertex: 4, Gray: 3, Black 4 Vertex: 3, Gray: 7, Black 8 Vertex: 5, Gray: 9, Black 12 Vertex: 6, Gray: 10, Black 11 |
SOLUTION
depth first search
Algorithm analysis
Construct an adjacency matrix from the
list of edges. Run a depth first search on a
disconnected graph. For each vertex v,
compute the values of the timestamps d[v] and f[v]. Then run the depth first search again and, in the order of traversing the
vertices, print the timestamps when it turns gray / black.
Example
Graph given in a sample, has the form:
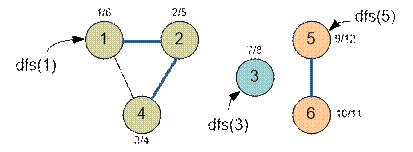
Algorithm
realization
Declare an
adjacency matrix m and arrays.
#define MAX 101
int m[MAX][MAX], d[MAX], f[MAX], used[MAX];
Depth
first search from the vertex v. Remember the entry / exit time to / from the vertex in d[v] / f[v].
void dfs(int v)
{
used[v] = 1;
d[v] = time++;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (m[v][i] && !used[i]) dfs(i);
used[v] = 2;
f[v] = time++;
}
Arrays d and f are already filled. Depth first search prints the values of
timestamps d[v] / f[v].
void dfs1(int v)
{
used[v] = 1;
printf("Vertex: %d, Gray: %d,
Black %d\n", v, d[v], f[v]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (m[v][i] && !used[i]) dfs1(i);
}
The main part of the program. Fill with zeroes the arrays. Read the number of vertices n.
memset(m, 0, sizeof(m)); memset(used, 0, sizeof(used));
scanf("%d", &n);
Using the
list of edges, construct an adjacency matrix.
while (scanf("%d %d", &a, &b) == 2)
m[a][b] = m[b][a] = 1;
Initialize
the time time = 1. Run depth first search on a disconnected
graph.
time = 1;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (!used[i])
dfs(i);
The next depth first search will print the timestamps d[v] / f[v] in the order
of the first visit to the vertices.
memset(used, 0, sizeof(used));
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (!used[i]) dfs1(i);
Java realization
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static int g[][], used[], d[], f[];
static int n, m, time = 1;
static void dfs(int v)
{
used[v] = 1;
d[v] = time++;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (g[v][i] == 1
&& used[i] == 0) dfs(i);
f[v] = time++;
used[v] = 2;
}
static void dfs1(int v)
{
used[v] = 1;
System.out.println("Vertex:
" + v + ", Gray " + d[v] + ", Black
" + f[v]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (g[v][i] == 1
&& used[i] == 0) dfs1(i);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
n = con.nextInt();
g = new int[n+1][n+1];
used = new int[n+1];
d = new int[n+1];
f = new int[n+1];
while(con.hasNextInt())
{
int a = con.nextInt();
int b = con.nextInt();
g[a][b] = g[b][a] = 1;
}
time = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (used[i] == 0) dfs(i);
used = new int[n+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (used[i] == 0) dfs1(i);
con.close();
}
}